|
【跟科学家一起读文献】CT双低篇 “跟科学家一起读文献”是对比剂学院重磅最近推出的全新环节。我们的高级应用团队的科学家们每月为您推荐和解读影像诊断方面的热点和实用文献,包括CT增强、MR增强和介入等方面。上期我们的主题是DCE-MRI 临床应用篇,这期我们高级应用团队的黄宁博士为您带来CT双低篇的分享。

黄宁博士 分别在清华大学及美国新泽西州立大学 (Rutgers University)获得生物医学工程专业的本科及博士学位,曾在在西门子美国研究院及中国研究院从事医学影像方面研究工作。目前在GE医疗生命科学PKRC团队进行DCEMRI,CT低剂量,CT灌注,影像组学等方面研究及临床合作,与国内放射科合作发表SCI文章十余篇。
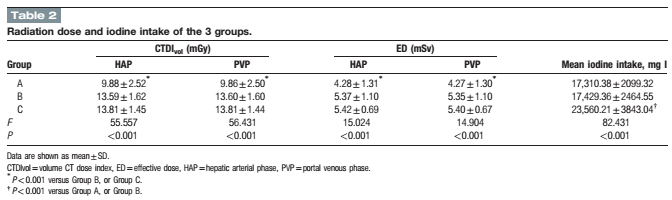
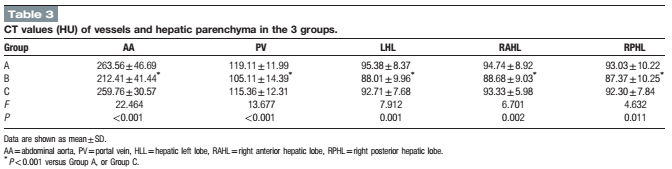
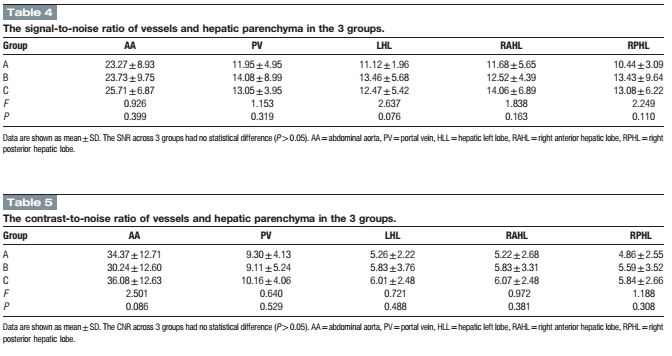
Double-low protocol for hepatic dynamic CT scan: Effect of low tube voltage and low-dose iodine contrast agent on image qualityXiuli Zhang, MD,a Shaodong Li, MD,a Wenlou Liu, MD,c Ning Huang, Ph.D.,d Jingjing Li, MD, PhD,a,b Li Cheng, MD,aand Kai Xu, MD, PhDa,b,∗ 徐州医学院附属医院 Medicine & #40;Baltimore& #41;. 2016 Jun; 95& #40;26& #41;: e4004. Published online 2016 Jul 1. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000004004 点击查看文献原文: Double_low_protocol_for_hepatic_dynamic_CT_scan_.38.pdf Double_low_protocol_for_hepatic_dynamic_CT_scan_.38.pdf ABSTRACT The radiation-induced carcinogenesis from computed tomography & #40;CT& #41; and iodine contrast agent induced nephropathy has attracted international attention. The reduction of the radiation dose and iodine intake in CT scan is always a direction for researchers to strive. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the feasibility of a “double-low” & #40;i.e., low tube voltage and low-dose iodine contrast agent& #41; scanning protocol for dynamic hepatic CT with the adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction & #40;ASIR& #41; in patients with a body mass index & #40;BMI& #41; of 18.5 to 27.9 kg/m2. A total of 128 consecutive patients with a BMI between 18.5 and 27.9 kg/m2 were randomly assigned into 3 groups according to tube voltage, iodine contrast agent, and reconstruction algorithms. Group A & #40;the “double-low” protocol& #41;: 100 kVp tube voltage with 40% ASIR, iodixanol at 270 mg I/mL, group B: 120 kVp tube voltage with filtered back projection & #40;FBP& #41;, iodixanol at 270 mg I/ mL, and group C: 120 kVp tube voltage with FBP, ioversol at 350 mg I/ mL. The volume CT dose index & #40;CTDIvol& #41; and effective dose & #40;ED& #41; in group A were lower than those in group B and C & #40;all P < 0.01& #41;. The iodine intake in group A was decreased by approximately 26.5% than group C, whereas no statistical difference was observed between group A and B & #40;P > 0.05& #41;. There was no significant difference of the CT values between group A and C & #40;P > 0.05& #41;, which both showed higher CT values than that in group B & #40;P < 0.001& #41;. However, no statistic difference was observed in the contrast-to-noise ratio & #40;CNR& #41;, the signal-to-noise ratio & #40;SNR& #41;, and image-quality scores among the 3 groups & #40;all P > 0.05& #41;. Near-perfect consistency of the evaluation for group A, B, and C & #40;Kenall's W = 0.921, 0.874, and 0.949, respectively& #41; was obtained by the 4 readers with respect to the overall image quality. These results suggested that the “double-low” protocol with ASIR algorithm for multi-phase hepatic CT scan can dramatically decrease radiation dose and iodine intake with adequate image quality in patients with BMI of 18.5 to 27.9 kg/m2. Keywords: contrast agent, hepatic dynamic CT, iterative reconstruction, low-dose CT 通过双低技术同时减少辐射剂量及对比剂摄入量,可以满足临床诊断的同时减少患者所受辐射伤害及肾损伤,是患者及放射学界期望得到的理想结果,也符合ALARA(As Low As Reasonable Achievable)原则。 这篇文章采集了128例肝脏CT患者,(BMI在18.5到27.9之间)分为3组。A组:双低组,100kVp管电压,碘克沙醇270(270mgI/ml),结合40%ASIR重建;B组:低碘剂量组,120kVp管电压,碘克沙醇270;C组:正常组,120kVp结合碘佛醇(350mgI/ml)。结果发现A组的CTDIvol及ED显著低于B组和C组,A组的碘摄入量相比于C组同时减少了26.5%。 而A组和C组之间,CT值之间并无显著差异,而两组均显著高于B组。三组之间评价指标,如对比噪声比CNR,信噪比SNR及主观评价分数并无显著性差异。4位放射医师独立评价,三组之间的一致性Kenall's 评分分别达到0.921, 0.874和 0.949, 显示很高的一致性。 文章结论认为,双低扫描方案结合叠代重建技术在腹部多期增强中可以显著降低辐射剂量及碘摄入量,并得到充分的图像质量。 
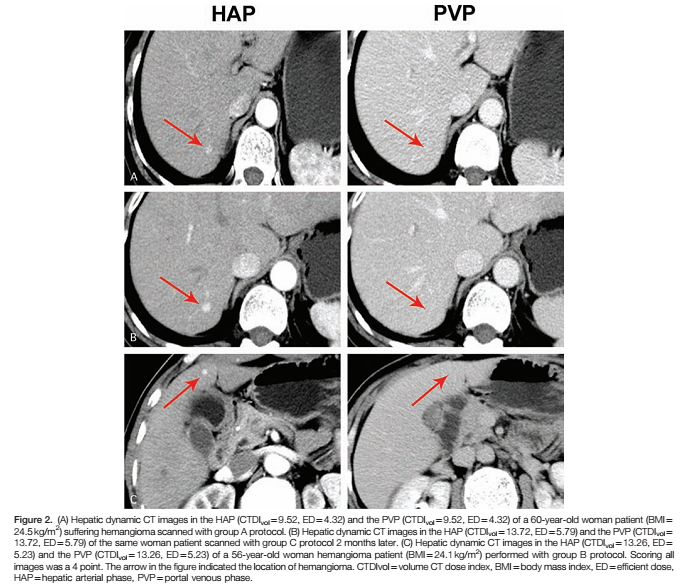
Comparison of Virtual Unenhanced CT Images of the Abdomen under Different Iodine Flow Rate Yongrui Li, Ye Li, Alan Jackson, Xiaodong Li, Ning Huang, Chunjie Guo, Huimao Zhang 吉林大学附属第一医院
SCI杂志:Abdom Radiol & #40;2016& #41;. doi:10.1007/s00261-016-0842-4
点击查看文献原文: Comparison of Virtual Unenhanced CT Images of the Abdomen under Different Iodine Flow Rate 吉大附一Abdominal Radiology.pdf Comparison of Virtual Unenhanced CT Images of the Abdomen under Different Iodine Flow Rate 吉大附一Abdominal Radiology.pdf ABSTRACT Objective: To assess the effect of varying iodine flow rate & #40;IFR& #41; and iodine concentration on the quality of Virtual UnEnhanced Images & #40;VUE& #41; of the abdomen obtained with dual-energy CT. Methods: 94 subjects underwent unenhanced and tri-phasic contrast enhanced CT scan of the abdomen, consisting: arterial phase & #40;AP& #41;, portal venous phase & #40;VP& #41; and delayed phase & #40;DP& #41; using dual energy CT. Patients were randomized into 4 groups with different iodine flow rates & #40;IFR& #41; or iodine concentration. VUE images were generated at 70 KeV. The CT values, image noise, SNR and CNR of aorta, portal vein, liver, liver lesion, pancreas parenchyma, spleen, erector spinae and retroperitoneal fat were recorded. Dose length product & #40;DLP& #41; and effective dose & #40;ED& #41; for an examination with and without plain phase scan were calculated to assess the potential dose savings. Two radiologists independently assessed subjective image quality using a five-point scale. The Kolmogorov-Smirnov Test was used first to test for normal distribution. Where data conformed to a normal distribution, analysis of variance was used to compare mean HU values, image noise, SNRs and CNRs for the 4 image sets. Where data distribution was not normal, a non-parametric test & #40;Kruskal-Wallis test followed by stepwise step-down comparisons& #41; was used. The significance level for all tests was 0.01 & #40;two-sided& #41; to allow for type 2 errors due to multiple testing. Results: The CT numbers & #40;HU& #41; of VUE showed no significant differences between the 4 groups & #40;p>0.05& #41; or between different phases within the same group & #40;p>0.05& #41;. VUE had equal or higher SNR and CNR than true unenhanced & #40;TUE& #41; images. VUE received equal or lower subjective image quality scores than unenhanced images but were of acceptable quality for diagnostic use. Calculated dose length product and estimated dose showed that the use of VUE in place of unenhanced images would be associated with a dose saving of 25%. Conclusions: VUE can replace conventional unenhanced images. VUE are not affected by varying iodine flow rates and iodine concentrations, and diagnostic examinations could be acquired with a potential dose saving of 25%. Keywords: computer tomography, Material Suppressed Iodine, iodine flow rate, virtual unenhanced imaging 摘要 目的:评估不同碘流率(IFR)和不同碘浓度对腹部双能量CT虚拟平扫(VUE)图像质量的影响 方法:94 位患者使用双能量CT扫描了腹部平扫及三期增强,包含动脉期AP,门脉期VP和延迟期DP。虚拟平扫采用70Kev图像重建。测量主动脉,门静脉,肝脏,肝脏病变,胰腺,脾脏,竖脊肌及腹膜后脂肪的CT值,图像噪声,SNR,CNR。计算包含及不包含平扫的三期增强的DLP及有效剂量ED。两位放射科医师使用5分法独立评价图像质量。使用Kolmogorov-Smirnov检验数据是否符合正态分布,对于符合正态分布的,ANOVA被用来比较不同组之间的CT HU值,图像质量,SNR和CNR;不符合正态分布的采用Kruskal-Wallis检验。 结果:4组间虚拟平扫VUE的CT值没有显著差异,不同时相之间也没有显著差异。相对于真实平扫,VUE的SNR和CNR相同或者更高,但VUE的主观质量评分不高于真实平扫TUE。如果使用VUE替代TUE,辐射剂量DLP及ED可以下降25%。 结论:VUE可以替代传统平扫图像。VUE不受不同的碘流率及碘浓度的影响,可以在不影响诊断准确性的情况下减少25%的辐射剂量。 过去很多研究也在探讨虚拟平扫是否能替代真实平扫以降低辐射剂量,但基本没有研究探讨不同碘流率的影响。本文的目的就是研究腹部双能量成像,不同碘流率及碘浓度对虚拟平扫图像质量的影响。 方法: 患者 2013年12月到2014年6月的104位患者被随机分为4组,分组如表一. 2.2扫描方法 扫描使用双能量CT & #40;Discovery CT 750HD, GE Healthcare, Waukesha, WI& #41;. 首先平扫,病人仰卧位,一个呼吸周期内扫描从肝顶到骼脊水平。接着采用双能量模式扫描3期。自动管电流调节,螺距0.984, 5 mm 层厚, 转速0.5 sec,FOV 38x38mm. 动脉期使用Smart Prep, ROI f置于腹主动脉根部,阈值100 HU. 触发10秒后开始扫描动脉期,动脉期30秒后扫描静脉期,90秒后扫描延迟期. 分组如下: Table 1:Injection protocols of different groups & #40;with fixed injection time of 20s& #41;
GROUP | n | Contrast Agent and concentration & #40;mg I/ml& #41; | Flow rate & #40;ml/s& #41; | IFR | Total iodine | A | 24 | Iohexol 350 | 4.0 | 1.4g I/s | 28 g | B | 22 | Iohexol 350 | 3.43 | 1.2g I/s, | 24 g | C | 26 | Iodixanol 320 | 4.375 | 1.4g I/s, | 28 g | D | 22 | Iodixanol 320 | 3.75 | 1.2g I/s, | 24 g |
注射后,4组都采用20ml盐水冲洗。 2.3图像重建 所有图像采用 40% AsiR重建. 不同碘流率下的VUEs 在70 keV下使用GE AW4.6工作站上标准的双能量物质分离得到. 2.4 图像评价 客观图像质量评价 对于以下部位,(1)腹主动脉(2)肝脏右页(3)脾脏(4)竖脊肌(5)腹膜后脂肪(6)门静脉(7)胰头(8)肝脏病变, 每个部位分布放置三个ROI,并测量图像噪声, SNR 和 CNR。 ROI的大小约1 cm2, 同一部位计算三个ROI的平均值. 进行双盲评估 主观打分 由两名有经验的放射科医师五分制双盲法分别打分,使用固定窗宽窗位 & #40;窗宽, 400 HU; 窗位, 40HU& #41;. 使用两者的平均值作为主观质量分数。图像质量>=3 认为满足诊断要求 2.5 评估放射剂量 2.6 统计分析 使用Kolmogorov-Smirnov检验数据是否符合正态分布,对于符合正态分布的,ANOVA被用来比较不同组之间的CT HU值,图像质量,SNR和CNR;不符合正态分布的采用Kruskal-Wallis检验。 3. 结果 4组间虚拟平扫VUE的CT值没有显著差异,不同时相之间也没有显著差异。相对于真实平扫,VUE的SNR和CNR相同或者更高,但VUE的主观质量评分不高于真实平扫TUE。 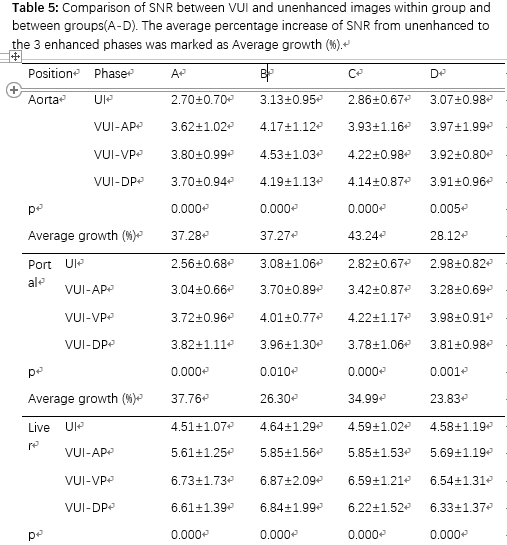
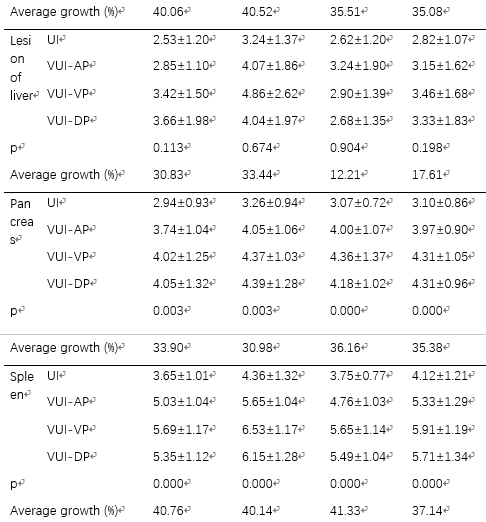
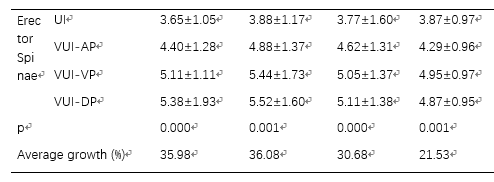
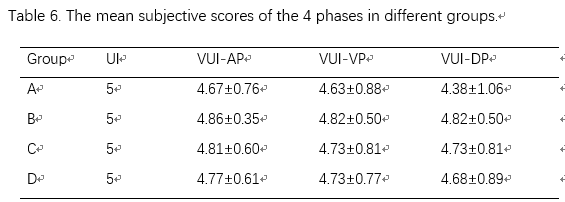
4. 讨论 本前瞻性研究说明,腹部VUE可以在不同碘流率及碘浓度下替代平扫,并大幅度降低辐射剂量。同时,VUE图像质量和平扫基本一致。 本研究主要目的是保证在临床中不同碘流率的变化,不会影响VUE的图像质量。之前没有研究考虑这方面的问题。虚拟平扫利用了不同物质不同的能谱曲线,采用了双物质分离的方法得到去除碘增强后的水图像,并可以降低金属伪影等。 5. 结论 从腹部多期增强计算的VUE 有潜力替代传统平扫图像, VUE的组织,血管等位置CT值和平扫在临床使用的碘流率和碘浓度的范围内都无明显区别。使用虚拟增强,临床诊断的多期增强可以降低辐射剂量25%左右。 文章来源:Li, Y., Li, Y., Jackson, A. et al. Abdom Radiol & #40;2016& #41;. doi:10.1007/s00261-016-0842-4
|