|
作者:Desiree E. Morgan 作者单位:Department of Radiology, University of Alabama at Birmingham, JTN452 619 South 19th Street, Birmingham, AL 35249, USA 本文发表于:Abdominal Imaging (2014) 39:108–134 翻译:Zheng Ying, M.D. 
上期回顾: CT双能成像可以对泌尿系结石的化学成分进行更好的定性,双源双能减影可以区分尿酸结石和非尿酸结石,能谱成像可以区分更多的结石成分。对肾肿物进行能谱碘浓度测定,可以大幅度提高肾脏病灶定性诊断的精度。肾癌转移灶的能谱碘浓度测定也有潜力成为抗血管增生治疗疗效评估的影像学生物标记物。 本期内容: 能谱CT在肾上腺疾病诊断中的应用价值
能谱CT在肾上腺疾病诊断中的应用价值 Adrenal applications
在对比增强CT检查中经常会偶然发现肾上腺病变[38]。可以根据肾上腺病变在平扫图像中的CT值来判定病变为良性腺瘤。 Incidental adrenal lesions are commonly found on contrast-enhanced CT examinations performed for other indications [38]. If unenhanced images are present, there are defined attenuation criteria to differentiate types of adrenal lesions and confirm a lesion as a benign adenoma.
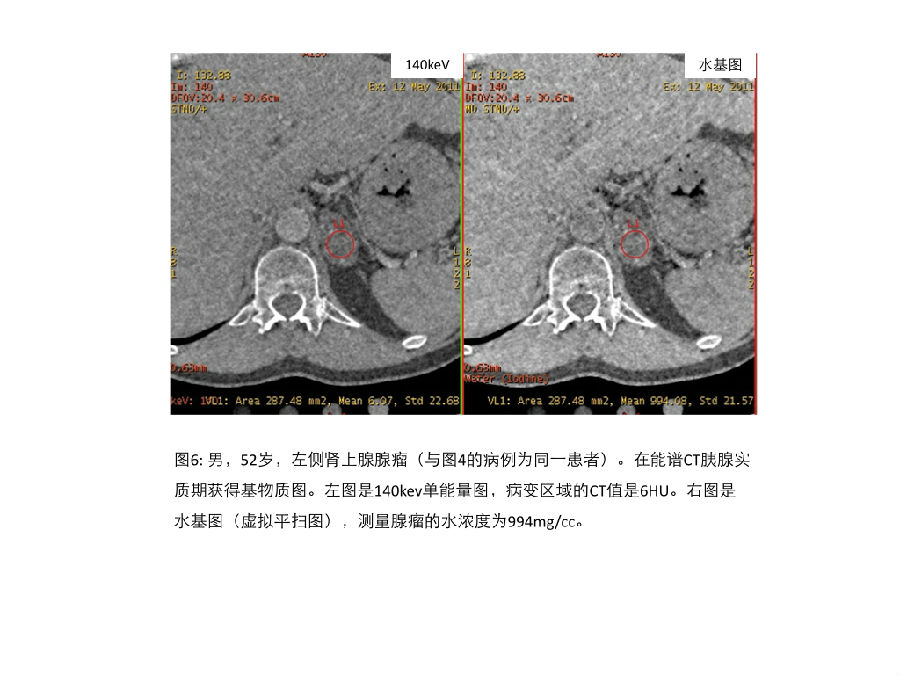
但是,有了CT能谱成像之后,即使不进行传统的CT平扫,也能通过能谱的虚拟平扫图像来确定肾上腺病变的性质。 However, even if conventional unenhanced images are not acquired, it may still be possible to characterize a lesion if the contrast enhanced CT was performed using a dual-energy technique.
Gnannt 等学者对42位患者51例病变进行评估,能谱成像的的虚拟平扫图像具有良好的准确性[39]。用传统CT平扫图像作为参考,通过两位独立研究者进行读片,能谱CT虚拟平扫图像对确认大于或者等于25px的良性病变的敏感性、特异性和准确性分别为95, 100, 97%和 91, 100, 95%。虚拟平扫图像与传统平扫图像的CT值之间没有显著差异。 Gnannt et al. [39] showed good accuracy of virtual unenhanced images generated on DECT in a study evaluating 42 patients with 51 lesions. Using conventional unenhanced CT as a reference, the sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy for DECT virtual unenhanced images for classifying a lesion >= 1 cm as probably benign were 95, 100, 97%, and 91, 100, 95%, respectively, for two independent readers. There were no significant differences in the mean HU values on virtual unenhanced compared to conventional unenhanced images.
Ho等学者的研究显示[40],对于肾上腺瘤的CT值,虚拟平扫图像与传统平扫图像之间没有显著的统计学差异(肾上腺瘤在虚拟平扫图像的CT值是10.3 ± 13.1,传统平扫图像的CT值是8.9 ± 10.4);对于转移性病变二者也无显著统计学差异(虚拟平扫图像的CT值是35.7 ± 6.0,传统平扫图像的CT值是32.6 ± 6.1)。重要的是,在上述每个研究中,没有恶性结节被误判。 Similarly, Ho et al. [40] reported no statistically significant difference in the mean Hounsfield Unit measurements of adenomas (10.3 ± 13.1 on virtual unenhanced vs. 8.9 ± 10.4 on conventional unenhanced images), or metastases (35.7 ± 6.0 on virtual unenhanced vs. 32.6 ± 6.1 on conventional unenhanced images). Importantly, no malignant nodules were misclassified in either study.
研究小组应用传统平扫图像和能谱特征性的水基图、脂肪基图和140keV图 对一组肾上腺富脂肪病变和乏脂肪病变进行了分析,证实了能谱的这些特征性参数和传统CT值之间具备很好的相关性。能谱CT可以提供确诊富脂质腺瘤的的诊断阈值,这个阈值具备很高的特异性。 Using rsDECT, our group evaluated arterial phase water(–iodine), fat(–iodine), and pseudo-unenhanced 140 keV images compared to conventional unenhanced scans in the same subjects and found strong correlation between these rsDECT variables and accepted single- energy MDCT attenuation values for high lipid-content and low lipid-content adrenal lesions. Clinically relevant thresholds on rsDECT that identified lipid-rich adenomas with high specificity were determined (Weber et al. (2012) presented to the Society of Abdominal Radiology, unpublished data).
《连载6》引用的参考文献: 38. Remer EM, Casalino DD, Bishoff JT, et al. (2012) ACR appropriateness criteria on incidentally discovered adrenal mass. Reston: American College of Radiology (ACR). http://guidelines.gov/ content.aspx?id=37940. 39. Gnannt R, Fischer M, Goetti R, et al. (2012) Dual-energy CT for characterization of the incidental adrenal mass: preliminary observations. AJR 198:138–144 40. Ho LM, Marin D, Neville AM, et al. (2012) Characterization of adrenal nodules with dual-energy CT: can virtual unenhanced attenuation values replace true unenhanced attenuation values? AJR 198:840–845 41. Kim YK, Park BK, Kim CK, Park SY (2013) Adenoma characterization: adrenal protocol with dual-energy CT. Radiology 267:155–163
|