|
作者:Desiree E. Morgan 作者单位:Department of Radiology, University ofAlabama at Birmingham, JTN452 619 South 19th Street, Birmingham, AL 35249, USA 本文发表于:Abdominal Imaging & #40;2014& #41; 39:108–134 翻译:Tony Lu 
上期回顾: 能谱CT在肝脏的应⽤用包括通过基物质图像的形态学观察和定量测量以及低keV单能量图像的形态学观察,增加肝脏病灶的检出。同时能谱CT还有助于便捷的评估肝脏病变局部治疗的治疗效果。
本期内容: 单源瞬切能谱CT在胰腺疾病诊断中的应用价值
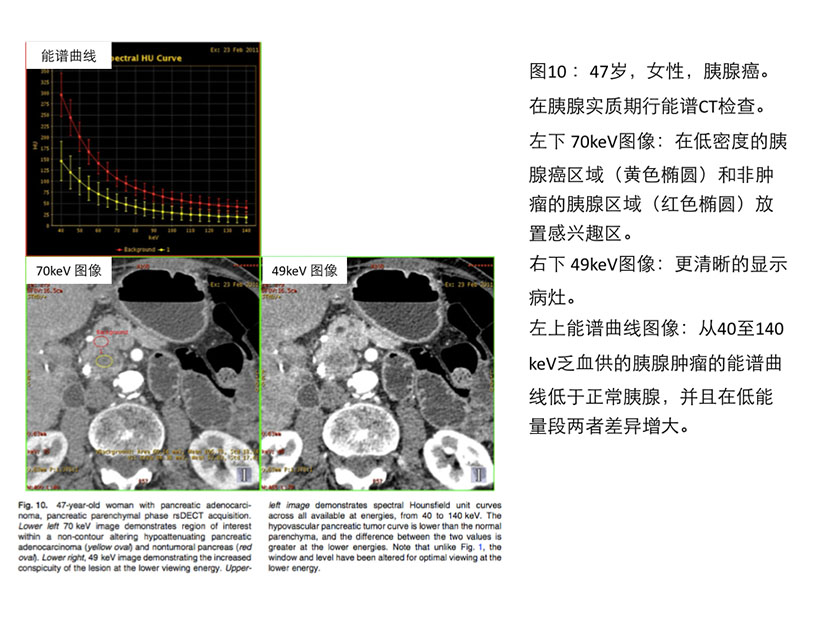
单源瞬切能谱CT在胰腺的应用 Pancreasapplications Macari的研究表明[53],相对于120kVp,门脉期80kVp的图像可以更为清晰的显示胰腺病变。Patel等在一个65例的大样本研究中[7],使用单源瞬切能谱CT在胰腺实质期进行能谱扫描,来评估70keV图像、最佳对比噪声比(CNR-optmized keV)图像、45keV图像对胰腺癌病变的显示。最佳对比噪声比(CNR-optmizedkeV)图像发现的胰腺病灶几乎是70keV图像的2倍,具有显著的统计学意义。值得注意的是,这个研究中的图像最佳对比噪声比的keV值的中位数是52keV(参见图10)。
Macari et al. [53] first showed that conspicuity of pancreatic adenocarcinoma wasgreater using 80 kVp compared to blended 120 kVp images on dsDECT obtained inportal venous phase. Patel et al. [7] used rsDECT acquired during pancreaticparenchymal phase to evaluate pancreatic adenocarcinoma lesion conspicuity in alarger population of 65 patients, comparing 70 keV images to contrast to noiseratio & #40;CNR& #41;-optimized keV images and 45 keV images. The statisticallysignificant increase of lesion contrast & #40;defined as HU difference betweentumoral and nontumoral pancreas& #41; at the CNR- optimized keV was nearly doublethat of the 70 keV image, the image typically used for routine PACS viewing.Notably, the median value of the CNR optimized images for the population was 52keV & #40;Fig. 10& #41;.
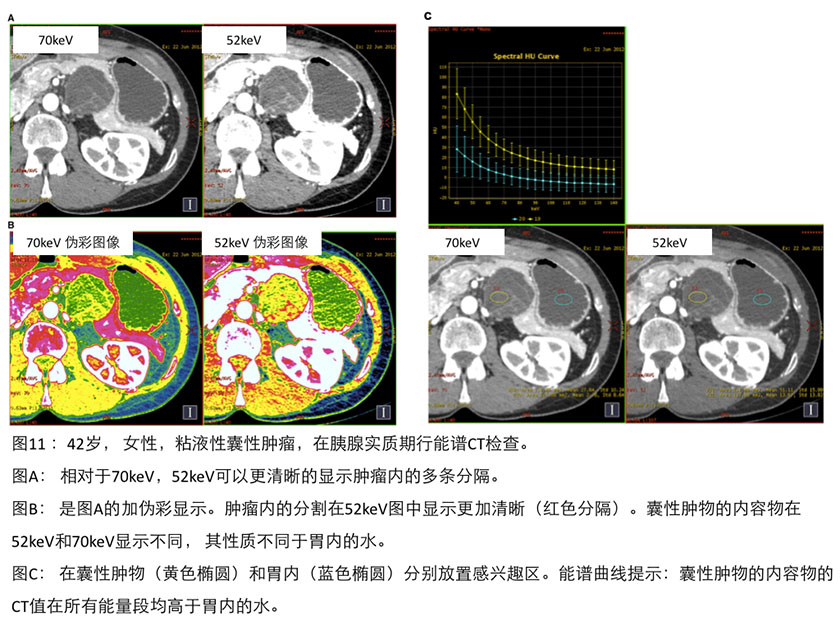
虽然早期的研究摘要记载了使用双能量CT研究胰腺神经内分泌肿瘤和胰腺囊性病变,但还没有对特定胰腺病灶进行双能成像的研究论文发表。相对于传统CT,能谱CT在提高胰腺病变评价方面显现出前途无量,因为能谱CT能够提高对胰腺富血供病变或囊性肿块复杂内部结构的清晰显示(参见图11)。
There is little lesion-specific published literature on other dual- energy applicationsin the pancreas; however, early experiences with pancreatic endocrine neoplasmsand cystic pancreatic lesions have been presented in abstracts. The technologyappears promising for improved evaluation compared to single-energy CT becauseof the potential gains in conspicuity of pancreatic hypervascular lesions or ofimproved visualization of complexity within cystic masses & #40;Fig. 11& #41;.
我们的研究发现利用碘基图可以评价小的或等密度的肿瘤(见图12),因为碘基图比70keV或更低keV的图像具有更好的低对比噪声比。Chu等研究者发现 [54],和双源双能减影图像相比,碘基图可提供更多的诊断信息:碘基图有助于鉴别囊性病变和实性病变,并可以更好的评价肿块与邻近血管的关系。
We have explored the use of iodine images for evaluation of small or isoattenuatingpancreatic neoplasms & #40;Fig. 12& #41;, since on rsDECT these images have lowercontrast noise ratios than 70 or lower keV images. Chu et al. [54] also foundthat iodine images had additional diagnostic yield compared to blended imageson a dsDECT system; in that study the iodine images helped to discriminate thecystic versus solid nature of a lesion, provided greater conspicuity and aclearer assessment of the relationship to nearby vessels.

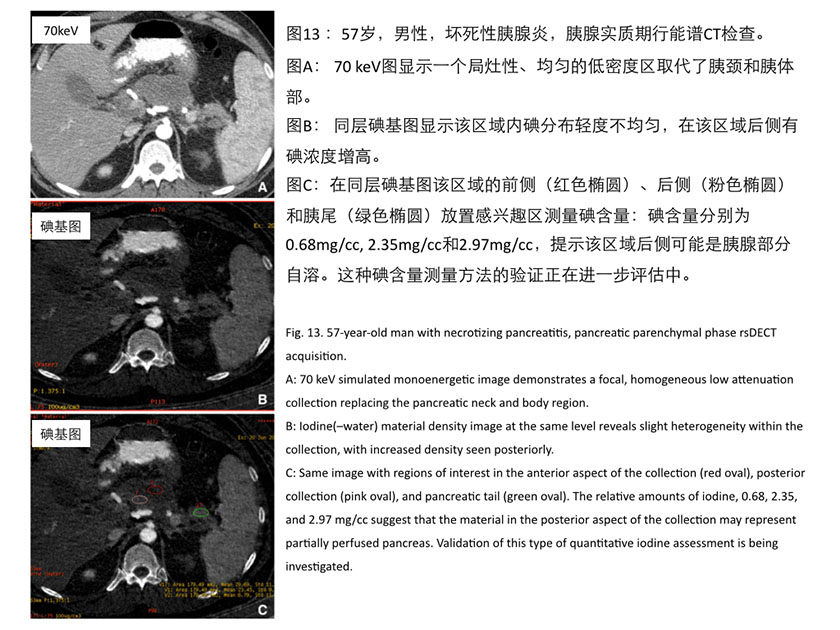
碘基图还有助于评价胰腺坏死,在急性胰腺炎的发作中对后腹膜的低密度物质集聚区进行分析,可以帮助判断是否存在胰腺自溶(见图13)。
Iodine images might be helpful for evaluation of patients with pancreatic necrosis& #40;Fig. 13& #41; to determine if perfused pancreas is present within acomplex retroperitoneal collection evolving during the course of an acutepancreatitis episode.
经过初期对肝脏和胰腺能谱CT的研究,我们已经在临床常规中发送70keV和52keV的图像到PACS,进行腹部多期能谱扫描的读片。这不仅增加了病变的显示率,而且在对比剂增强效果不佳时,较低能量段的keV图像可以增加肿瘤与非肿瘤组织之间的对比。
In our practice, as a result of preliminary hepatic and pancreatic investigations wenow routinely send 52 keV simulated monoenergetic images, in addition to 70 keVimages to PACS for routine clinical interpretation of multiphasic abdominalrsDECTs. We have found that not only does this increase lesion conspicuity, butalso, in the case of a suboptimal bolus, the gain in contrast differencebetween the tumoral and nontumoral tissues can be recovered in part by viewingat the lower energies.
利用低keV图像进行CT血管成像,可以为外科医生提供细节更丰富的CT血管造影图像。在我们的临床常规中,除了发送70keV和52keV两组单能量图像到PACS外, 碘基图和水基图也常规地作为单独序列发送到PACS供阅片观察。
Creation of CT angiograms from the lower keV source images provides more robust surfacerendered images for referring surgeons. In addition to the two sets ofsimulated monoenergetic images, the water& #40;–iodine& #41; and iodine& #40;–water& #41; materialdecomposition basis pair images are routinely sent to PACS as separate seriesand viewed for clinical interpretation.
对于肝脏或胰腺切除手术,可能会使用胆道金属支架或手术金属夹,这些金属物体会产生金属伪影,影响胰腺的观察。使用单源瞬切能谱CT的金属伪影去除序列(MARS)或采用140keV图像都可以去除金属伪影,更好的观察胰腺(见图14)。
Finally, the use of a dedicated metal artifact reduction algorithm & #40;MARS& #41; using rsDECT,or simply viewing the images at 140 keV provides more optimal viewing of thepancreas around metallic bile duct stents or surgical clips that may be presentfrom prior hepatic or pancreatic resections & #40;Fig. 14& #41;, similar to reduction ofmetal artifacts around joint prostheses [8]. 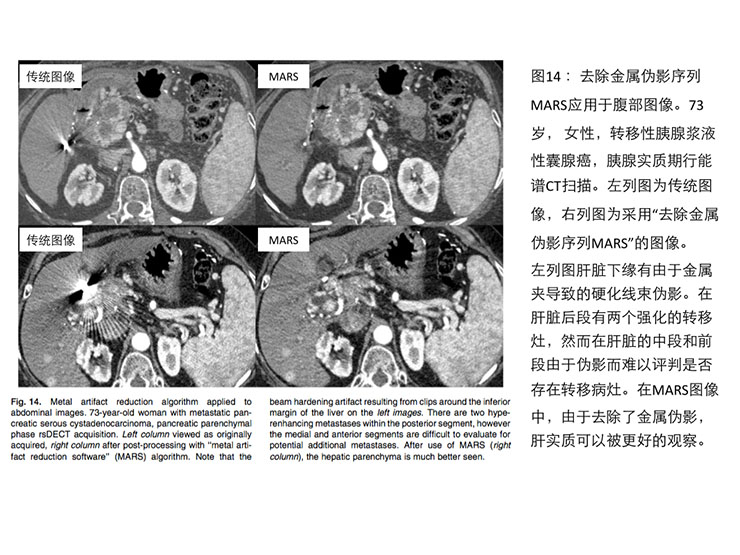
《连载8》引用的参考文献:
7. Patel BN, Thomas JV, Lockhart ME, Berland LL, Morgan DE & #40;2013& #41;Single-source dual-energy spectral multidetector CT of pancreaticadenocarcinoma: optimization of energy level viewing significantly increaseslesion contrast. Clin Radiol 68& #40;2& #41;:148–154 8. Pessis E, Campagna R, Sverzut JM, et al. & #40;2013& #41; Metal artifactsreduction using monochromatic images from spectral CT: evalua- tion of pediclescrews in patients with scoliosis. Eur J Radiol . doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2013.02.024 53. Macari M, Spieler B, Kim D, et al. & #40;2010& #41; Dual-sourcedual-energy MDCT of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: initial observations with datagenerated at 80 kVp and at simulated weighted-average 120 kVp. AJR 194:W27–W32 54. Chu AJ, Lee JM, Lee YJ, et al. & #40;2012& #41; Dual-source,dual-energy multidetector CT for the evaluation of pancreatic tumours. BritishJ Radiol 85:e891–e898
|